In the ever-evolving landscape of medical science and technology, researchers and healthcare professionals are continually seeking innovative ways to improve the lives of individuals suffering from neurological conditions. Among these emerging technologies, Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (aVNS) has emerged as a promising avenue for the treatment of nervous system disorders. In this article, we will explore the potential of aVNS in the context of neurological conditions and shed light on recent scientific studies that have provided valuable insights into its efficacy.
Understanding Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation
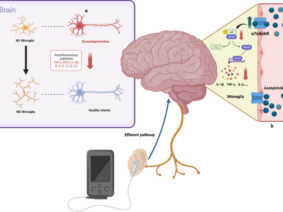
Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation, or aVNS, represents a novel approach to neuromodulation. Unlike traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS), aVNS does not involve invasive implantation, making it an attractive option for patients and clinicians alike. The vagus nerve is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system and plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and inflammation. Stimulating this nerve, either through the traditional approach or via the ear, has shown promise in addressing a wide range of neurological conditions.
Research Progress and Anatomical Insights
Recent research in the field of aVNS has provided valuable insights into the anatomical structure and parameters of the vagus nerve, as well as its role in treating nervous system diseases. Yang and Jia’s study, published in the Journal of Biosciences and Medicines in 2023, reviewed the advancements in aVNS research. They emphasized the absence of a unified standard for aVNS treatment parameters for nervous system diseases, highlighting the need for further investigation in this area [1].
This underscores the importance of ongoing research efforts aimed at defining optimal treatment parameters and protocols for aVNS. Establishing these standards will enable healthcare providers to offer more consistent and effective care to patients with neurological conditions.
The Promise of aVNS in Disorders of Consciousness
One particularly intriguing area of aVNS research is its potential application in patients with disorders of consciousness (DOC). A study conducted by Jang and Cho in 2022 reviewed six studies investigating the effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) in patients with DOC [2]. The findings suggest that taVNS holds promise as an effective and safe intervention for individuals with DOC, with positive results reported in the majority of studies. Neuroimaging studies have also indicated potential changes in the brain following taVNS, shedding light on the neurological mechanisms involved.
However, the study highlights several limitations, including a shortage of research in this area, a lack of control or sham groups in some studies, and a lack of standardization in treatment schedules and electrical stimulation parameters. These limitations underscore the need for further research to address these challenges and refine the application of aVNS in the context of DOC.
Prospects for the Future
Looking ahead, ongoing clinical trials and research studies are poised to unlock the full potential of aVNS in treating neurological conditions. For instance, a clinical trial by Vitello et al., published in the International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology in 2023, aims to assess the therapeutic effects of taVNS in patients with disorders of consciousness, investigate neural mechanisms, and evaluate long-term efficacy [3].
Additionally, a study by von Wrede et al. in 2021 explored the effects of taVNS in subjects with refractory epilepsy. Their findings indicated that short-term taVNS induced modifications in epileptic brain networks, enhancing network stability without negatively affecting cognition or behavior [4].
In conclusion, Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation represents a promising avenue for the treatment of neurological conditions. While there is still much to learn and standardize in terms of treatment parameters and protocols, the growing body of research in this field is paving the way for more effective and innovative treatments. As scientists and clinicians continue to explore the potential of aVNS, it offers hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals facing neurological challenges.
References:
- Yang, J., & Jia, N. (2023). Advances of Research on Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Treatment of Nervous System Diseases. Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, 11, 1-14.
- Jang, S. H., & Cho, M. J. (2022). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in disorders of consciousness: A mini-narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore), 101(50), e31808.
- Vitello, M. M., Briand, M. M., Ledoux, D., Annen, J., El Tahry, R., Laureys, S., Martin, D., Gosseries, O., & Thibaut, A. (2023). Transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders of consciousness: Protocol for a double-blind randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 23(2).
- von Wrede, R., Rings, T., Schach, S., Helmstaedter, C., & Lehnertz, K. (2021). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation induces stabilizing modifications in large-scale functional brain networks: towards understanding the effects of taVNS in subjects with epilepsy. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 7906.