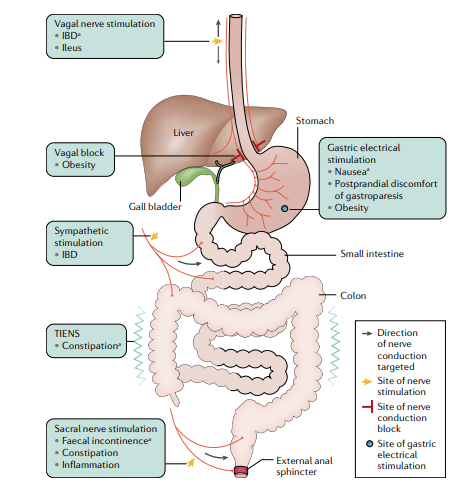
The gastrointestinal tract, a complex network of nerves and muscles, plays a central role in the body’s digestive processes. Recent advances in medical science have unlocked a promising avenue for aiding gastrointestinal health through bioelectric neuromodulation. This groundbreaking technique utilizes non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation to support digestive function and general wellness through nervous system modulation. The potential of this method stems from the gastrointestinal tract’s extensive connections with the central nervous system, which can be harnessed to improve outcomes.
The Gastrointestinal Conundrum
Gastrointestinal health has long posed significant challenges for medical professionals. Traditional approaches have shown variable success, leaving users searching for more effective and less invasive alternatives. This is where bioelectric neuromodulation enters the spotlight.
A Gateway to Gastrointestinal Solutions
While sacral nerve stimulation has been found successful in addressing fecal incontinence, the potential applications of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation are far-reaching. The digestive system’s intricate nerve connections provide a gateway to explore and manipulate the neurological mechanisms behind gastrointestinal challenges. Research has shown that nerves are instrumental in modulating inflammation in the intestine, a vital clue to the puzzle of gastrointestinal health.
The Power of Vagal Nerve Stimulation
One remarkable revelation in this field is the anti-inflammatory potential of vagal nerve stimulation. Recent trials have shown positive effects of this approach in specific instances.The vagus nerve activation may support balanced inflammatory responses, which are thought to influence digestive comfort, opening the door to more effective methods.
Beyond Inflammation:
High-frequency current pulses applied to the vagus nerve has been explored for its potential impact on appetite signaling and metabolic rhythms. By blocking signaling from the stomach to the brain, appetite can be regulated. However, outcomes have been mixed, highlighting the need for further research to optimize this approach.
The Path to Enhanced Success
To maximize the success of bioelectric neuromodulation methods, researchers are working on several fronts. First and foremost is a deeper understanding of the targeted nerve pathways within the gastrointestinal system. By pinpointing these pathways, professionals can tailor stimulation protocols to specific issues, may complement existing wellness strategies through non-invasive neural engagement. Moreover, user selection is a crucial aspect of optimization, ensuring that the right candidates benefit most from this groundbreaking method.
Conclusion
Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation represents a promising frontier in gastrointestinal well-being. As bioelectric neuromodulation technology continues to evolve, it offers renewed hope for individuals grappling with a range of issues. By understanding the intricate neural pathways and their functions and refining stimulation protocols, we are edging closer to unlocking the full potential of this transformative method. With ongoing research and trials, non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation has the potential to revolutionize gastrointestinal health, providing a brighter future for countless users.
References:
- Payne, S.C., Furness, J.B. & Stebbing, M.J. Bioelectric neuromodulation for gastrointestinal disorders: effectiveness and mechanisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16, 89–105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0078-6